Return Stacked® Academic Review
Managing Beta Exposures in Portable Alpha Strategies
Authors
Peter van Dooijeweert, Graham Robertson
Man Institute
Managing Beta Exposures in Portable Alpha Strategies
Key Topics
return stacking, portable alpha, diversification, leverage, managed futures, trend following, risk management, portfolio construction, capital efficiency
The Case for Active Risk Management in Leveraged Strategies
To address these issues, van Dooijeweert and Robertson propose incorporating volatility scaling and trend-following techniques into the investment process. By dynamically adjusting portfolio exposures in response to changing market conditions, investors can enhance risk-adjusted returns, improve margin management, and achieve better drawdown control. This active approach not only bolsters capital efficiency but also offers robust diversification, aligning well with the principles of return stacking, which seeks to improve capital efficiency and diversification.
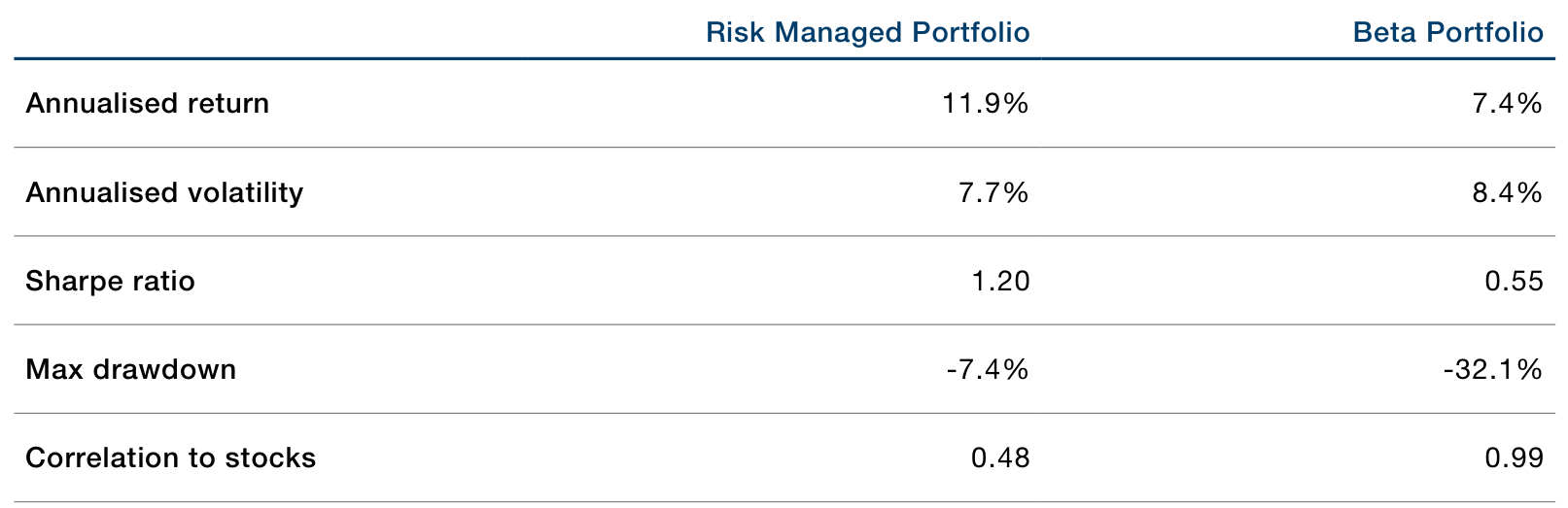
Comparative Performance and Drawdown Insights
The authors demonstrate the benefits of active risk management through a comparative analysis of an actively managed portfolio versus a traditional beta portfolio, both modeled as “60/40” portfolios with 60% equity and 40% bond exposure.
Figure 1: Actively Risk-Managed Portfolio Exhibits Less Severe Drawdowns Than Beta Portfolio (Original: Figure 6)
Source: Man Group database; date range: 1 January 1995 to 31 August 2020.
Simulated performance is not indicative of future results. Returns may increase or decrease as a result of currency fluctuations.
The performance, volatility and/or other information on the portfolios is simulated. The simulation has been created by ‘back testing’ a systematic trading model to historical data. Since the trades have not been executed, the published results may have under-or over-compensated for the impact, if any, of certain market factors, such as lack of liquidity. The synthetic track record is subject to change without notice as models develop over time. The performance results provided herein are based on simulations with trading costs estimated using internal slippage models. Portfolios are net of examples of fees of 1%, in order to better represent the fee and cost structure of an example fund.
“Beta portfolio” represented by a 60/40 portfolio based on 60% MSCI World Net Total Return and 40% Barclays Capital Global Aggregate Bond index rebalanced monthly. The composite is an appropriate benchmark for the strategy for performance comparison purposes. World stocks are represented by MSCI World Net Total Return Index.
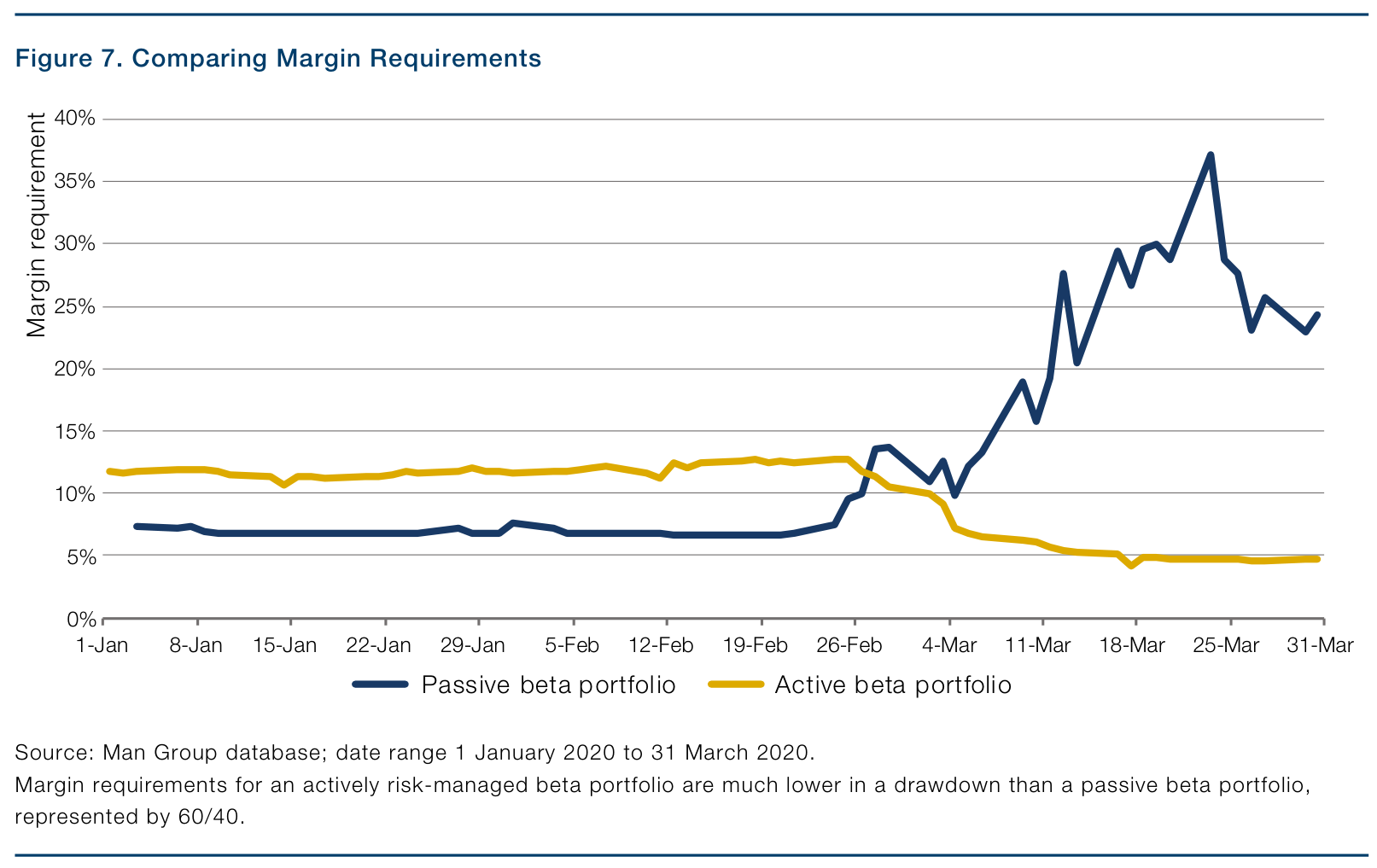
Enhancing Margin Efficiency and Liquidity Management
Figure 2: Comparing Margin Requirements (Original: Figure 7)
Implications for Return Stacked Portfolio Solutions
By actively managing beta exposures through techniques like volatility scaling and trend-following, investors can reduce the volatility of their core asset allocations. This creates a more stable foundation for stacking additional return streams without disproportionately increasing risk. The inclusion of strategies such as managed futures and trend-following can further enhance diversification and risk-adjusted returns, as discussed in this article on trend following.
Moreover, effective margin management, as demonstrated in the paper, aligns with the goals of return stacking by freeing up capital for additional investments. Reducing margin requirements through active risk management allows for greater flexibility in allocating capital to alpha-generating strategies, optimizing the overall risk-return profile of the portfolio.
Key Takeaways
“Managing Beta Exposures in Portable Alpha Strategies” provides valuable insights into how active risk management can enhance the performance of leveraged investment strategies. By adopting dynamic techniques such as volatility scaling and trend-following, investors can:
- Improve risk-adjusted returns by adapting to changing market conditions.
- Achieve better drawdown control, reducing the impact of market downturns.
- Enhance diversification through lower correlations with traditional asset classes.
- Optimize margin management, increasing capital efficiency and flexibility.
These principles are highly relevant to modern portfolio construction techniques like return stacking, where the efficient layering of multiple return streams is essential. By actively managing beta exposures, investors can build more resilient and efficient portfolios, better equipped to navigate the complexities of today’s financial markets.