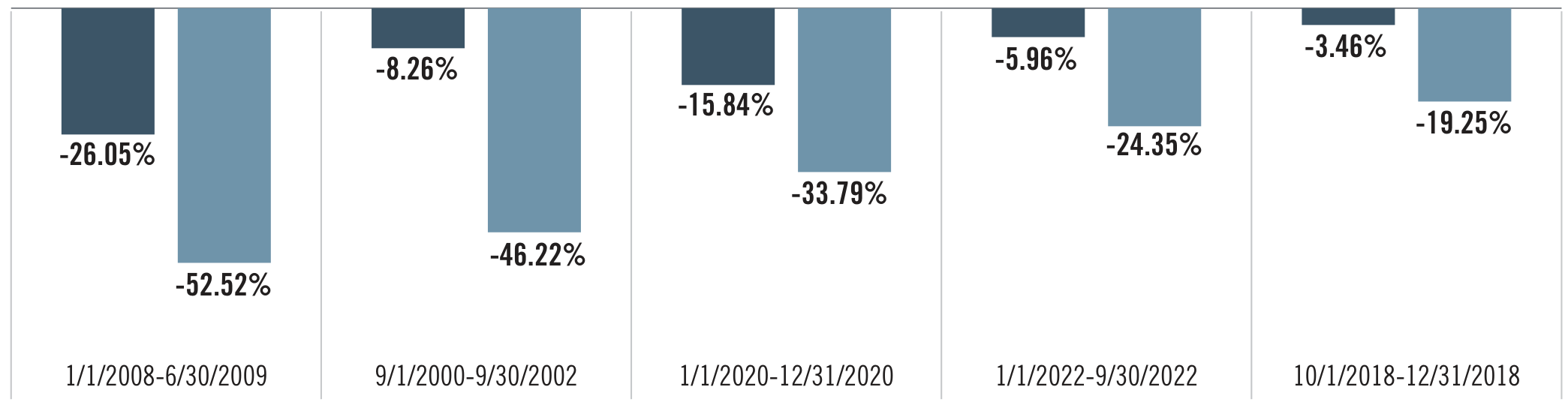Return Stacked® Academic Review
An Introduction to Merger Arbitrage
Authors
Roy Behren, Michael Shannon
An Introduction to Merger Arbitrage
Key Topics
return stacking, portable alpha, diversification, risk management, portfolio construction, capital efficiency
Exploring the Merger Arbitrage Strategy
In “An Introduction to Merger Arbitrage,” Roy Behren and Michael Shannon examine merger arbitrage as an investment strategy that seeks to profit from the successful completion of corporate mergers and acquisitions. This approach involves purchasing the stock of a company being acquired and, in certain cases, shorting the stock of the acquiring company. The goal is to capture the spread between the current market price and the deal price offered by the acquirer.
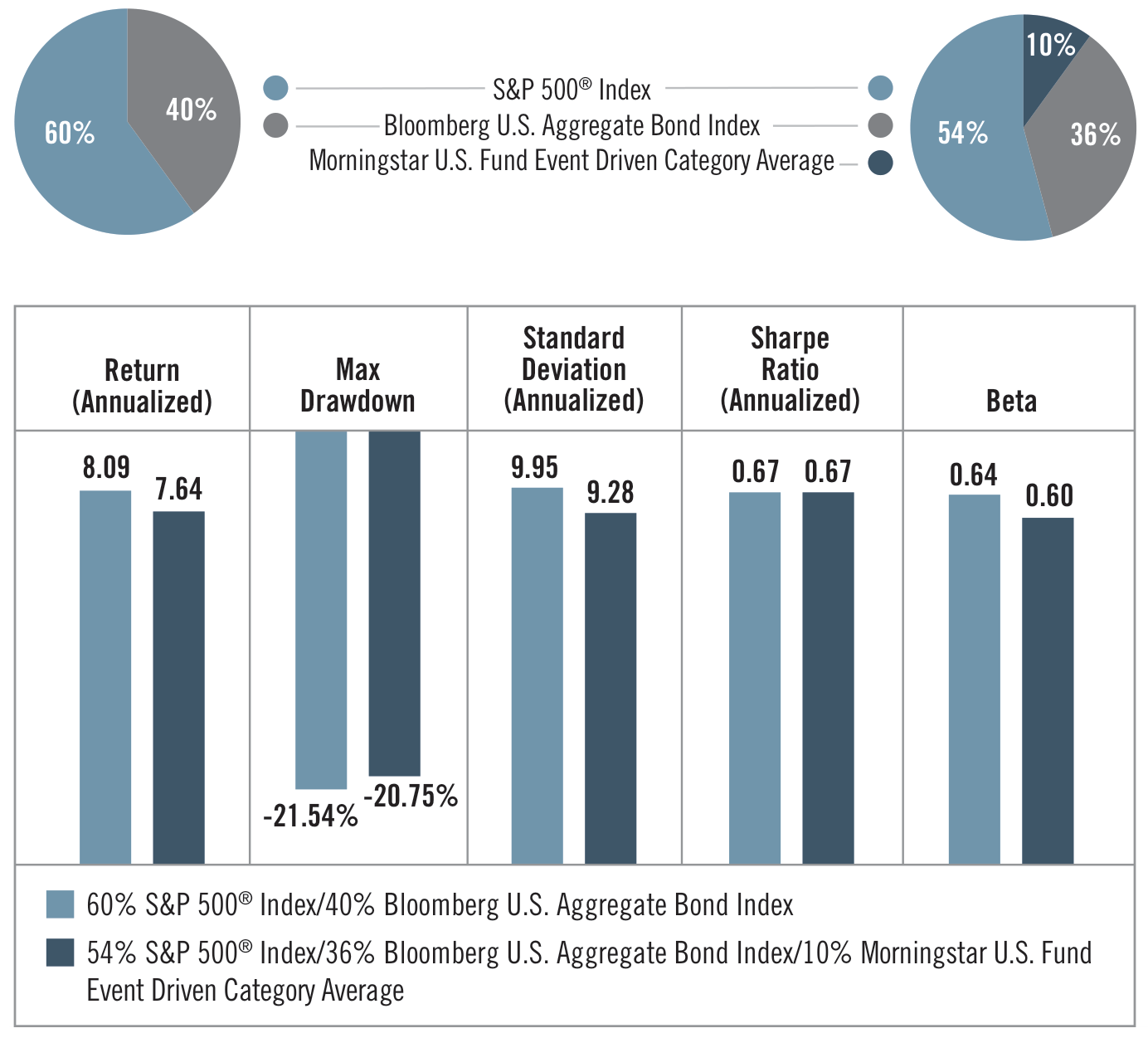
Merger arbitrage is characterized by its focus on deal-specific factors rather than broader market movements. The returns are driven by the outcomes of individual transactions, which are influenced by regulatory approvals, shareholder votes, and other idiosyncratic risks. This results in a low correlation with traditional asset classes, making merger arbitrage a potential tool for enhancing portfolio diversification and improving risk management.
Empirical Evidence Supporting Merger Arbitrage
Figure 1: Portfolio Performance Comparison (Original: Figure 1)
Figure 2: Performance During Major Market Downturns (Original: Figure 5)
Integrating Merger Arbitrage into Return Stacked Portfolios
This strategy can also complement portable alpha approaches, where the goal is to generate alpha—excess returns above a benchmark—without increasing beta exposure to the market. Since merger arbitrage returns are driven by deal-specific factors, they can provide alpha that is uncorrelated with market movements, aiding in risk management and volatility reduction.
The low correlation and unique return drivers of merger arbitrage make it a valuable addition to a diversified portfolio, potentially enhancing overall performance while mitigating risks associated with market downturns.