Return Stacked® Academic Review
A Half Century of Macro Momentum
Authors
Jordan Brooks
AQR Capital Management White Paper
A Half Century of Macro Momentum
Exploring Macro Momentum Strategy
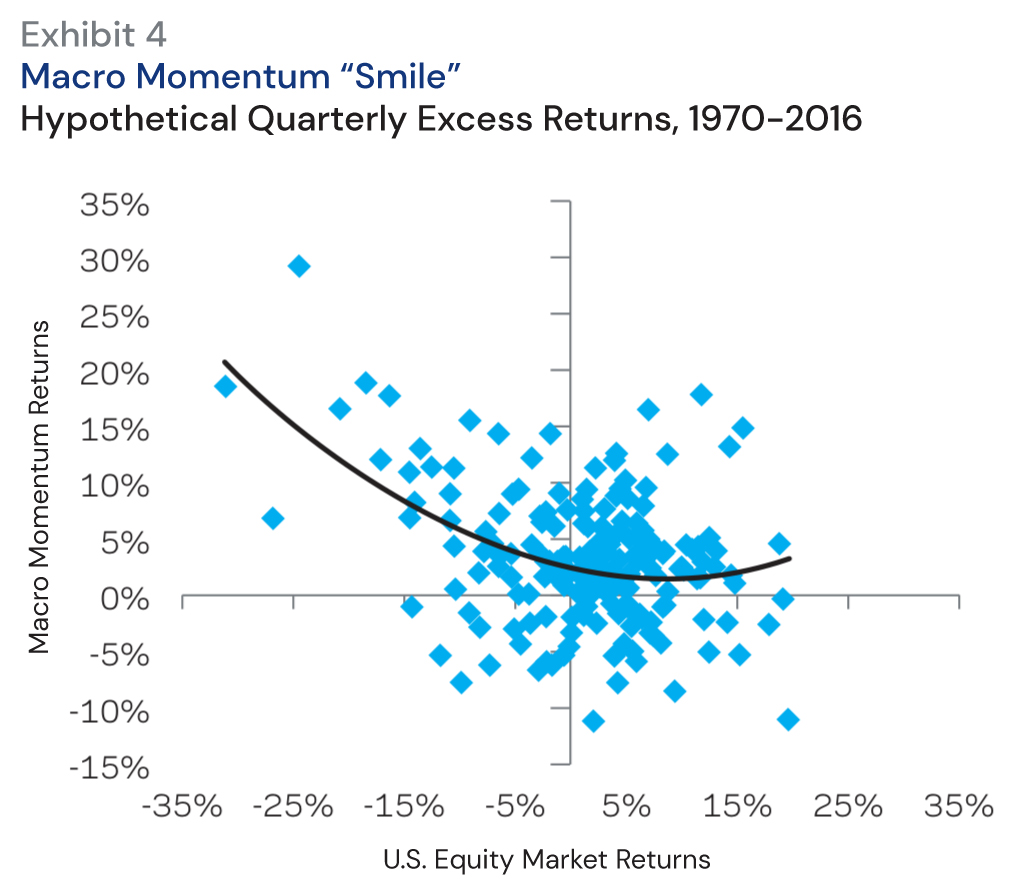
In “A Half Century of Macro Momentum,” Jordan Brooks of AQR Capital Management examines a systematic approach to global macro investing known as macro momentum. This strategy leverages fundamental macroeconomic trends to inform investment positions across various asset classes, including global equities, currencies, government bonds, and interest rates. By capitalizing on markets’ tendency to underreact to new information, macro momentum aims to exploit opportunities arising from shifts in key economic indicators.
The strategy focuses on four primary macroeconomic themes:
- Business Cycle: Changes in real GDP growth forecasts.
- International Trade: Movements in spot foreign exchange rates against export-weighted baskets.
- Monetary Policy: Variations in the front end of the yield curve.
- Risk Sentiment: Fluctuations in equity market excess returns.
By tracking one-year changes in these indicators, the macro momentum approach constructs portfolios that are positioned to benefit from ongoing economic trends.
Performance Insights and Resilience
A central finding of the paper is the macro momentum strategy’s robust performance over nearly five decades, encompassing varied economic environments such as recessions, wars, stagflation, and significant interest rate shifts. Notably, the strategy demonstrates the capacity to deliver positive returns with low correlation to traditional asset classes, highlighting its potential as a diversification tool.
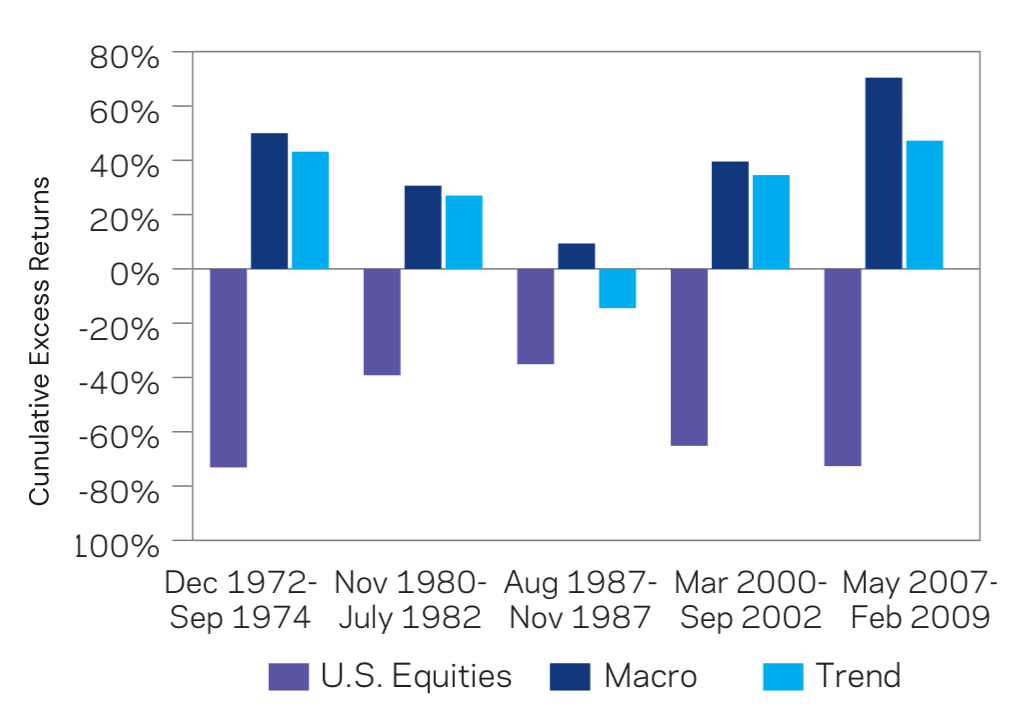
Figure 1: Macro Momentum's Performance in Equity Drawdowns (Original: Figure 4)
Source: AQR, Bloomberg, DataStream, Citi, Reuters, and IFS. U.S. Equity Market is measured by the S&P 500. See the Appendix for details on the simulation. Returns are gross of fees and transaction costs. Hypothetical data has inherent limitations, some of which are disclosed herein.
As shown in Figure 1, during the ten worst quarters for equities since 1970, when the S&P 500 averaged a -19.9% return, the macro momentum strategy delivered an average excess return of 13.7%. This inverse relationship indicates that macro momentum tends to perform exceptionally well during significant equity market downturns, providing a valuable hedge while still participating in gains during bull markets.
Comparing Macro Momentum and Trend-Following Strategies
While both macro momentum and trend-following strategies aim to exploit market underreactions, they operate through different mechanisms. Macro momentum is grounded in fundamental economic trends, whereas trend-following—often associated with managed futures – relies on price trends.
Figure 2: Diversification Benefits During Equity Market Drawdowns (Original: Figure 8)
Source: AQR, Bloomberg, DataStream, CRIF, Reuters, and IFS. See the Appendix for details on the universe. Returns are gross of fees and transaction costs. Hypothetical data has inherent limitations, some of which are disclosed herein.
Figure 2 illustrates that both strategies have historically provided strong performance during equity market drawdowns. However, their performance patterns aren’t identical, reflecting their different underpinnings. For instance, during rapid market crashes like in 1987, macro momentum remained resilient due to its positioning based on economic fundamentals, while trend-following struggled.
The correlation between macro momentum and trend-following is approximately 0.4, indicating that while related, they offer significant diversification benefits when combined. Incorporating both strategies can improve risk-adjusted returns, reduce maximum drawdowns, and enhance portfolio resilience.
For a deeper understanding of trend-following strategies, refer to this article.
Integrating Macro Momentum into Return Stacked Portfolios
Return stacking involves layering multiple, uncorrelated return streams on top of a core portfolio allocation by utilizing leverage, enhancing capital efficiency. Each “stack” represents a distinct source of return, contributing to a more robust and diversified portfolio.
Macro momentum aligns well with return stacking principles. Its low correlation with traditional assets and other alternative strategies makes it an ideal candidate for adding a differentiated return stream without significantly altering the portfolio’s overall risk profile. By employing leverage, investors can “stack” macro momentum onto existing allocations, potentially improving returns without additional capital investment.
For investors interested in enhancing diversification and capital efficiency, macro momentum can be combined with other strategies, such as portable alpha approaches. These involve seeking alpha through skill-based strategies while maintaining the beta exposure of traditional assets. An introduction to portable alpha can be found here.
Additionally, integrating macro momentum with carry-based strategies – which exploit the yield differential across assets—can further enhance portfolio diversification. For more on carry strategies, see this article.
Key Takeaways
Jordan Brooks’ “A Half Century of Macro Momentum” underscores the efficacy of a systematic global macro strategy grounded in fundamental economic trends. The macro momentum strategy’s historical resilience, especially during equity market downturns, and its low correlation with traditional asset classes, make it a compelling addition to diversified portfolios.
Incorporating macro momentum into a return-stacked framework allows investors to leverage multiple uncorrelated return streams, enhancing potential returns while mitigating risks. The strategic use of leverage in return stacking facilitates the layering of these strategies, optimizing capital efficiency.
By considering macroeconomic fundamentals in investment decisions and employing strategies like macro momentum, investors can build more resilient portfolios capable of navigating various market conditions.