Return Stacked® Academic Review
Demystifying Managed Futures
Authors
Journal of Investment Management, Vol. 11, No. 3 (2013), pp. 42-58
Demystifying Managed Futures
Key Topics
return stacking, portable alpha, diversification, trend following, managed futures, bonds, equities, yield, risk management, portfolio construction, capital efficiency
Unveiling the Mechanics of Managed Futures and Trend-Following Strategies
In “Demystifying Managed Futures,” Brian Hurst, Yao Hua Ooi, and Lasse Heje Pedersen provide a comprehensive analysis of managed futures and their underlying performance drivers. The study explores how straightforward, implementable time series momentum strategies can effectively explain the returns of managed futures funds and commodity trading advisors (CTAs). By analyzing data from January 1985 to June 2012 across 58 liquid futures and currency forwards – including commodities, equity indices, bonds, and currencies – the authors shed light on the mechanisms that make managed futures a valuable component of modern investment portfolios.
The paper challenges the perception that managed futures are overly complex by demonstrating that their returns can be largely attributed to trend-following strategies, specifically time series momentum. This approach involves taking positions based on the asset’s own past returns, capitalizing on the continuation of price trends. The authors attribute the effectiveness of these strategies to market behaviors such as initial under-reaction to news and subsequent delayed over-reaction, which create exploitable trends.
Visualizing Trend Dynamics and Performance Patterns
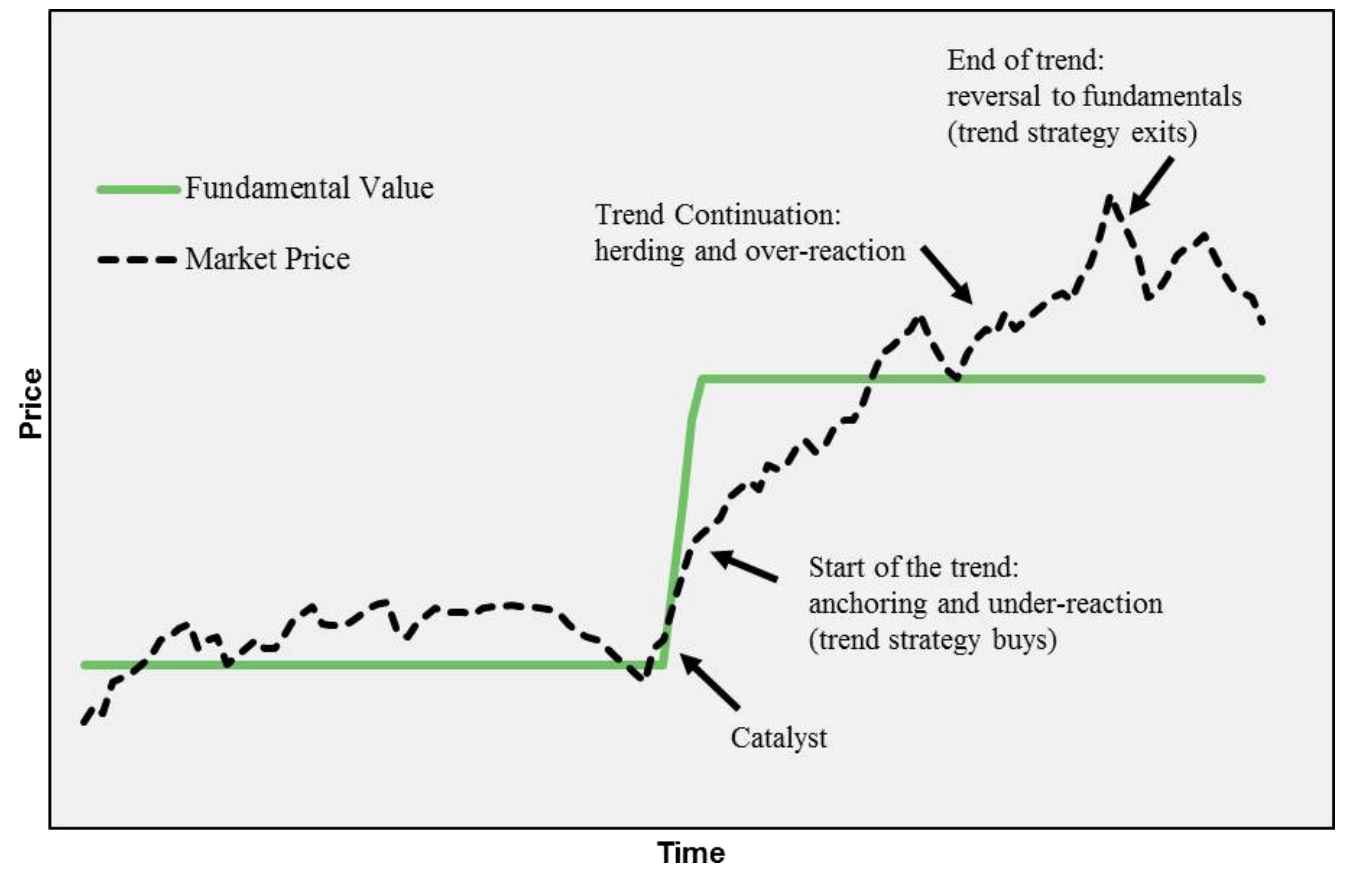
To illustrate the operational dynamics of trend-following strategies, the authors present the “life cycle” of a market trend.
Figure 1: Stylized Life Cycle of a Trend (Original: Figure 1)
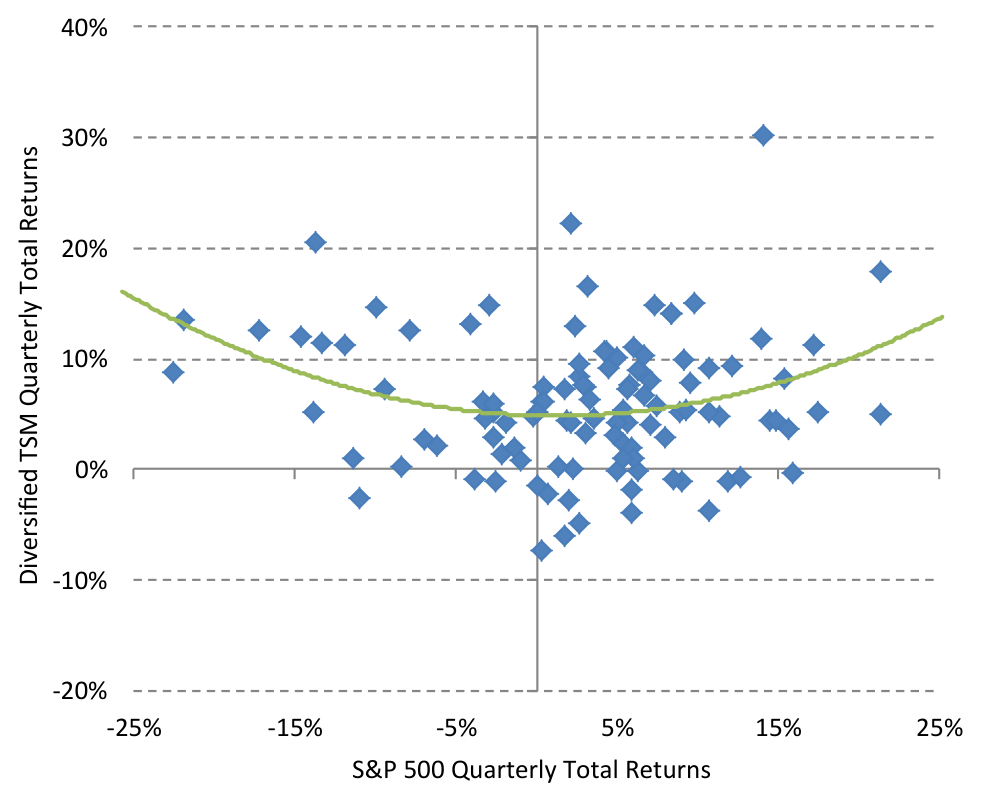
The performance characteristics of time series momentum strategies relative to the equity market are further examined.
Figure 2: Time Series Momentum "Smile" (Original: Figure 4)
Figure 2 plots the quarterly returns of a diversified time series momentum strategy against the S&P 500 from 1985 to 2012, revealing a “smile” pattern.
The “smile” pattern indicates that time series momentum strategies tend to perform well during periods of significant positive or negative market returns, while yielding modest results in flat markets. This characteristic underscores the potential of these strategies to provide crisis alpha by generating positive returns during extreme market conditions, both bullish and bearish.
Enhancing Portfolios with Time Series Momentum and Return Stacking
Incorporating trend-following strategies aligns with the concept of portable alpha, where investors seek to add sources of alpha that are independent of market movements. By integrating time series momentum into their portfolios, investors can achieve greater diversification and potentially improve risk-adjusted returns. The ability of these strategies to perform during extreme market conditions enhances portfolio resilience and capital efficiency.
However, practical considerations such as fees, transaction costs, and rebalancing frequency can impact net performance. Efficient execution and cost management are crucial to realizing the benefits of trend-following within a return stacked framework. Investors must balance the trade-offs between rebalancing frequency and transaction costs to optimize returns.
Final Thoughts on Managed Futures and Portfolio Diversification
For investors aiming to enhance portfolio yield and build resilience against market volatility, integrating trend-following strategies within a diversified, return stacked approach can offer significant benefits. Understanding and applying the concepts outlined in the paper enables investors to navigate the complexities of modern markets, improve risk management, and construct more robust portfolios capable of thriving across varying market environments.