Return Stacked® Academic Review
Trend-Following and Risk Factor Diversification in 2022 and 2023: A Tale of Two Extremes
Authors
Quantica Capital
Quantica Quarterly Insights
Understanding the Dynamics of Trend-Following Performance
In the ever-evolving financial markets, investors continuously seek strategies that can navigate changing environments. Trend following is one such strategy, designed to capitalize on sustained price movements across various asset classes. However, its performance is not consistent over time, and understanding the factors driving these fluctuations is crucial for effective portfolio integration.
Quantica Capital’s recent research delves into the relationship between trend-following performance, the number of independent risk factors, and investment universe diversification. By contrasting the markedly different market environments of 2022 and 2023, the study sheds light on how the underlying risk factor structure influences trend-following success.
In 2022, the SG Trend Index, a benchmark for trend-following CTAs, achieved a record net return of +27.3%. This exceptional performance was driven by a few strong systemic risk factors affecting multiple markets and asset classes. Conversely, 2023 presented challenges for trend-followers, with the SG Trend Index posting a negative return of -4.1%. Quantica attributes this underperformance to a market environment characterized by numerous idiosyncratic risk factors, each impacting trends across a diverse range of individual markets.
Analyzing Risk Factors Through Principal Component Analysis
To unravel the relationship between trend-following performance and risk factors, the authors employ Principal Component Analysis (PCA). PCA decomposes a strategy’s returns into independent statistical risk factors, known as principal components. Each principal component represents a combination of the underlying instruments, allowing for the measurement of their contributions to the strategy’s returns.
Applying PCA to a generic trend-following strategy, the researchers calculate the effective number of independent risk factors influencing performance each year, using the concept of Shannon entropy. A lower number indicates dominance by a few factors, while a higher number suggests a fragmented set of drivers.
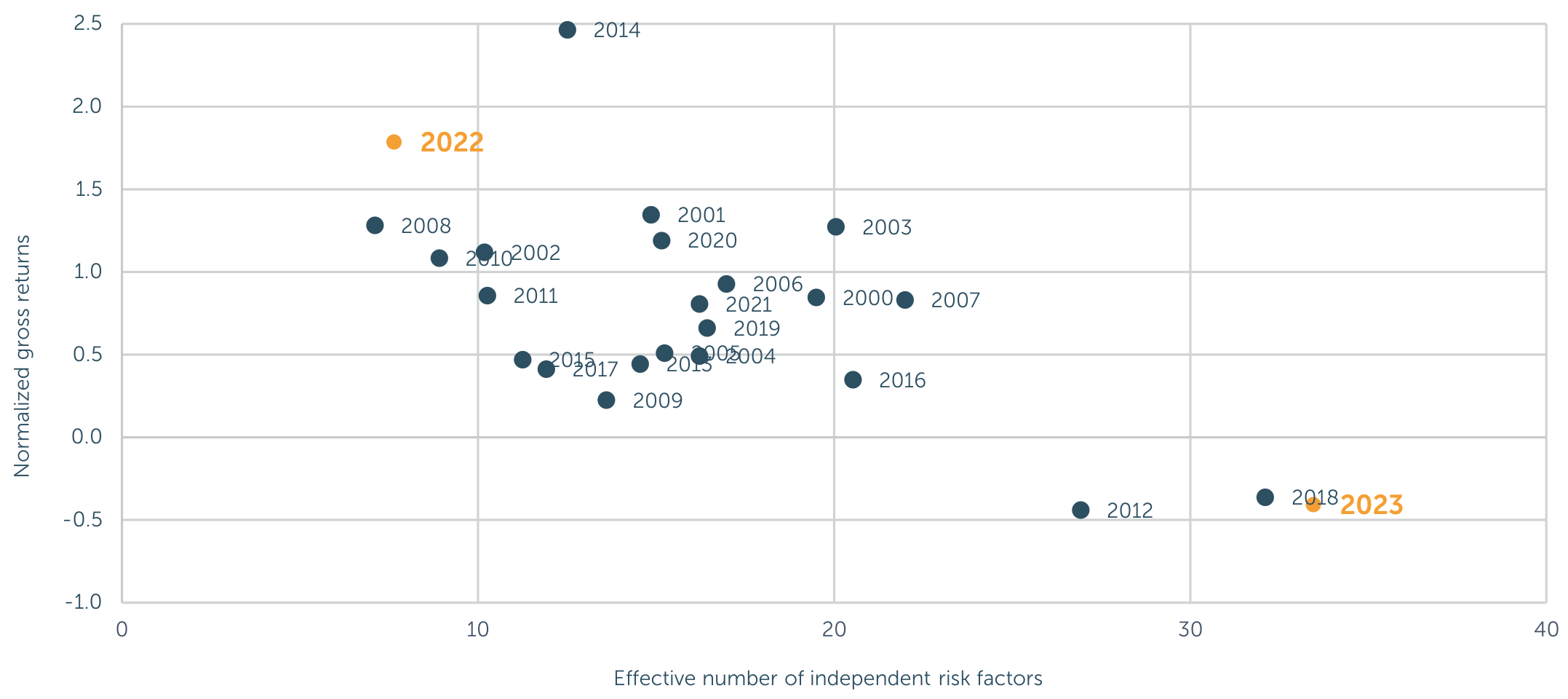
The analysis reveals a striking inverse relationship between performance and the number of risk factors. In 2022, with strong performance, the effective number of independent risk factors was only 8. This indicates that a few dominant factors were responsible for most returns. In contrast, 2023 saw an effective number of 33 risk factors, correlating with underperformance.
Figure 1: The Inverse Relationship Between Trend-Following Performance and the Effective Number of Risk Factors (Original: Figure 4)
The Importance of Investment Universe Diversification
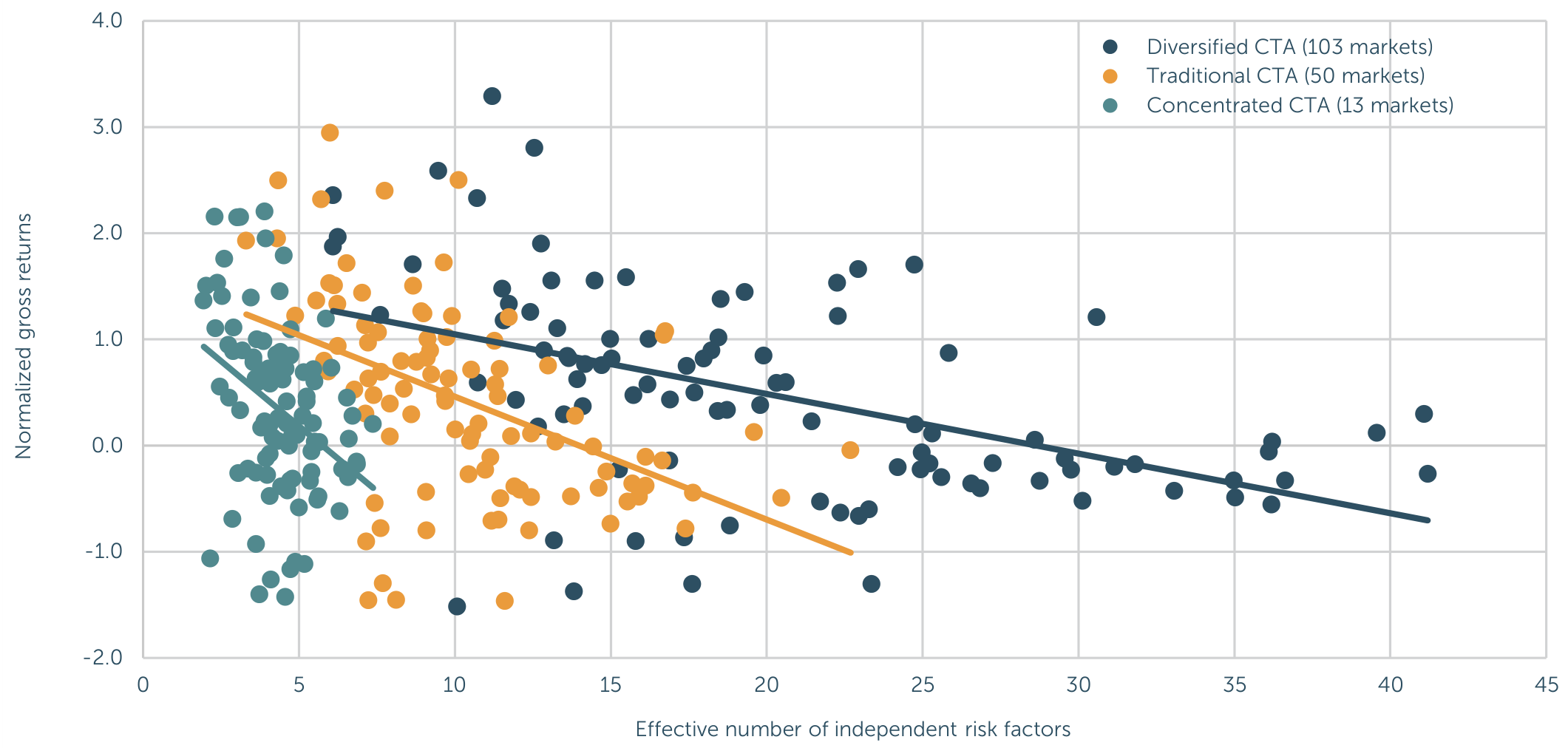
The study also explores how investment universe diversification can mitigate challenges in environments with many independent risk factors. The authors posit that a more diversified investment universe might better capture the diverse trends driven by idiosyncratic factors, enhancing overall performance.
To test this hypothesis, they compare the performance of a generic trend-following strategy across three different investment universes:
- Diversified CTA Universe: 103 liquid futures markets.
- Traditional CTA Universe: 50 ultra-liquid futures contracts.
- Concentrated CTA Universe: 13 most liquid and representative global futures markets.
Figure 2: Relationship Between Trend-Following Performance, Universe Diversification, and Effective Number of Risk Factors (Original: Figure 5)
Implications for Return Stacked Portfolios
In environments dominated by a few systemic risk factors, a return stacking approach might emphasize strategies that effectively capture these broad trends, potentially focusing on trend-following strategies with concentrated investment universes. Conversely, in periods characterized by numerous idiosyncratic risk factors, incorporating a wider range of strategies across a more diversified investment universe becomes crucial. This aligns with the principles of diversification in return stacking, which is explored in depth in Diversification 2.0: Understanding Return Stacking and the Evolution of Portfolio Construction.
Moreover, leveraging strategies like portable alpha can enhance capital efficiency within a return stacked portfolio. By overlaying alpha-generating strategies on top of a core portfolio, investors can seek additional returns without increasing the overall risk significantly. This concept is detailed in Portable Alpha: Leveraging Uncorrelated Returns.
Understanding the dynamics of risk factors is also essential when incorporating managed futures and trend-following strategies into a return stacked portfolio. These strategies can provide diversification benefits and potential returns during different market regimes, as discussed in Managed Futures and Trend Following.
Conclusion: Navigating Market Complexities with Diversification
For investors, especially those employing return stacking strategies, this means recognizing when to emphasize diversification and when a concentrated approach might suffice. In market environments dominated by a few systemic factors, concentrated trend-following strategies can be highly effective. However, as markets become driven by numerous idiosyncratic factors, broadening the investment universe and diversifying across multiple strategies becomes essential.
Incorporating these insights can enhance the resilience and robustness of investment portfolios. By dynamically adjusting allocations based on the prevailing market environment and leveraging strategies like portable alpha and managed futures, investors can better navigate the complexities of the financial landscape.
As markets continue to evolve, a nuanced understanding of risk factors, coupled with a flexible approach to diversification, will be key to achieving long-term investment success.